Sugar is a form of carbohydrate that comes in a wide variety of sugars, many of which we often study. Some sugars are known as monosaccharides, which are simple sugars having a straightforward structure. Disaccharides are some sugars that are created when two monosaccharides link together. Reducing sugars and nonreducing sugars are the two categories into which sugars can be categorized based on their chemical behaviors. The key difference between reducing and non reducing sugar is that Reducing sugars consists of free aldehyde or ketone groups, whereas nonreducing sugars do not.
In this article, we have shared the key difference between reducing and non reducing in detail along with the difference between reducing and non reducing sugar a level, so that you can understand both types of sugars easily.
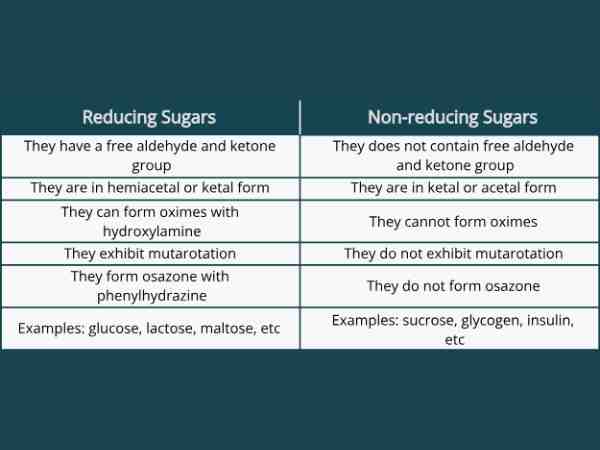
The Major Difference Between Reducing And Non-Reducing Sugars Along With Examples
Due to the presence of free ketone or aldehyde groups, reducing sugars are carbohydrates that can function as reducing agents. These are sugars because they have the same sweet flavor as other sugars. In addition, certain disaccharides are all monosaccharides, which are the types of reducing sugar.
Reducing sugars have this as one of their distinctive qualities and their examples include lactose and maltose as disaccharides as well as glucose, fructose, and galactose as monosaccharides.
Nonreducing sugars are carbohydrates that lack free ketone or aldehyde groups, making them incapable of acting as reducing agents. Nonreducing sugars do not produce any molecules with an aldehyde group in basic aqueous environments.
The Benedict’s Test
Here is the test which might help you to find out the difference between reducing and non reducing sugar:
Test for Reducing Sugar
- Benedict’s reagent should be added to the sample solution in the test tube. Benedict’s reagent includes copper (II) sulphate ions, which give the solution a blue color.
- Heat the test tube in the water bath or water beaker by bringing it to a boil.
- You can see colored precipitate forming in the presence of reducing sugar because copper (II) sulphate is converted to copper (I) oxide, which is insoluble in water.
- To ensure that there is enough copper (II) sulphate present to react with any sugar present in the sample, Benedict’s solution must be used in excess.
- A positive test result shows a change in color somewhere along a color scale from blue (implying no reducing sugar), through green, yellow, and orange (inferring the existence of low to medium solution of reducing sugar) to brown or brick-red (implying the existence of a higher solution of reducing sugar)
Testing for Non-reducing sugars
- The sample being tested should be mixed with dilute hydrochloric acid and heated in a water bath that has been brought to a boil for a few minutes.
- To neutralize the solution, use sodium hydrogen carbonate.
- To learn when the solution has been neutralized, use a suitable indicator such as a red piece of litmus paper. After that, add a little more sodium hydrogen carbonate because Benedict’s test requires slightly alkaline conditions.
- Perform Benedict’s test as usual After that you need to add Benedict’s reagent to the sample being tested and heat it in a water bath that has been brought to a boil for a few minutes. A color change will reveal the existence of non-reducing sugar in the concentration formed.
RELATED – WHAT IS THE MAJOR DIFFERENCE BETWEEN MAT DEGREE AND M. ED DEGREE?
Difference Between Reducing And Non Reducing Sugars Biology
We are aware that conventional meals like fruits, cereals, and dairy products contain sugars, starches, and fiber, which are classified as carbohydrates. Carbohydrates come in a variety of forms, including monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides however the most basic type of carbohydrates are monosaccharides. They are therefore referred to as the most fundamental type of carbohydrate.
When two monosaccharides, that is, monosaccharides, combine to generate disaccharides, and sugars (carbohydrate molecules), the result that comes is a disaccharide. According to their structural makeup, sugars (disaccharides) are now classified as reducing or non-reducing. Reducing sugars have free aldehyde or ketone groups, but non-reducing sugars don’t, and this is the primary difference between reducing and non reducing sugar biology (the two types of sugars). Thus, determining that reducing disaccharides have free aldehyde or ketone groups and non-reducing disaccharides do not is possible.
Difference Between Reducing Sugars And Non Reducing Sugars In Chemistry
Reducing and non-reducing sugars are terms used to describe the ability of sugars to reduce certain chemicals. The key difference between reducing and non reducing sugar in chemistry is that reducing sugars possess a free aldehyde or ketone group that can undergo a reaction with substances like Benedict’s reagent, causing a color change whereas, Non-reducing sugars lack such groups and thus cannot react with Benedict’s reagent directly. Common examples of reducing sugar are glucose and fructose and non-reducing sugar include sucrose and lactose.
To test for non-reducing sugars, a hydrolysis step is needed to break them down into their constituent reducing sugars. This hydrolysis step involves adding dilute acid to break the glycosidic bond. In summary, the key difference between reducing and non reducing sugar lies in their chemical structure and their ability to undergo specific reactions.
FAQs
What are reducing sugars and non-reducing sugars?
Ans. Reducing sugars have a particular functional group that enables them to react and reduce other compounds. Since non-reducing sugars lack this group, they must first be broken down to conduct comparable reactions.
How can I identify reducing sugars?
Ans. You can identify reducing sugars By observing how reducing sugars respond to tests like Benedict’s reagent, Fehling’s solution, or Tollens’ reagent. They change color or produce precipitation when reduced. By hydrolyzing non-reducing sugars into reducing sugars first, non-reducing sugars can be identified.
Why are reducing sugars called ‘reducing’?
Ans. Sugars that can “reduce” other substances by contributing electrons during reactions are known as reducing sugars. When certain sugars react with particular chemicals, the electron transfer causes observable changes in the reagents, such as color changes or precipitation.
What about non-reducing sugars? Why can’t they reduce other substances?
Ans. To provide electrons in processes, non-reducing sugars are deficient in the aldehyde or ketone groups required. Direct reduction is prevented by the glycosidic bonds in these molecules. Before they may participate in reactions like color changes with tests like Benedict’s reagent, they must first be broken down into their component-reducing sugars through hydrolysis.
What’s an example of reducing sugar?
Ans. One of the best examples of reducing sugar is glucose as it has an aldehyde group, which can give electrons during chemical processes. This property enables glucose to interact with chemicals like Benedict’s reagent, causing color alterations or precipitation, demonstrating its reducing nature.
RELATED – PEICE OR PIECE : WHICH ONE IS CORRECT?
The Final Words
The major difference between reducing and non-reducing sugars lies in their chemical structure and reactivity. To offer electrons and cause color changes or precipitation, reducing carbohydrates, such as glucose and fructose, have aldehyde or ketone groups. These groups are absent from non-reducing sugars like sucrose and lactose, which must undergo hydrolysis to become reduced and take part in comparable processes. For correct carbohydrate analysis and biochemical research, it is essential to comprehend the difference between reducing and non reducing sugar with example.
We hope that you found this article interesting and that it helped you clear all your queries regarding the difference between reducing and non reducing sugar.
Popular Search Terms
ROW VS COLUMN, LABLE OR LABEL, “SPELLING DILEMMA” WITHDRAWL OR WITHDRAWAL, What does ACT stand for?, Unveiling the Difference Between Long-Termism and Short, Fluffy French Bulldog Uncommon?, How do I choose Medicine Interview Tutors?, Differences Between Oil and Butter.


